Objective assessment of inter-annual changes in the duration of arctic melting season is hampered by short term weather conditions and a short term circa 14/15 day pseudo-periodic variation in ice coverage.
Simply taking the individual days with min/max coverage each year will be highly sensitive to such perturbing signals and does not provide a useful indication of the state of the ice on an annual basis. Since daily ice data is available, it is more appropriate to use the full dataset to extract a weather free annual variation.
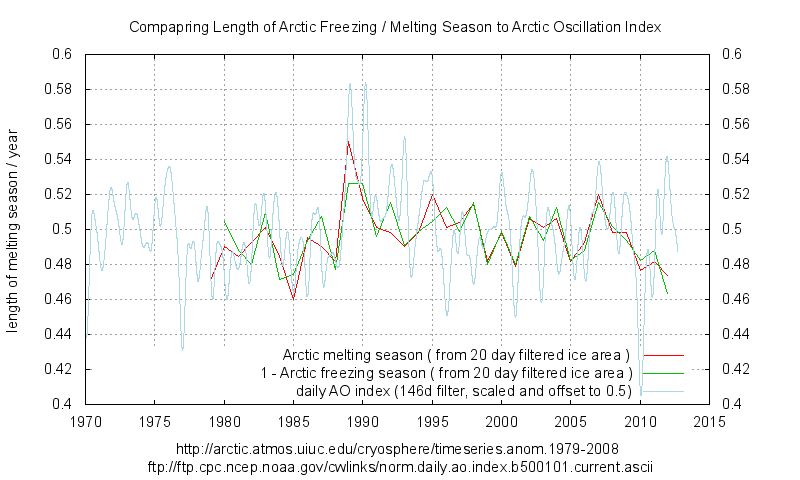
Gaussian filters of varying length were applied to establish stable results for the zero-crossing point of the rate of change of arctic sea ice area.
The zero crossing points were used as min/max dates to determine both the melting and freezing periods.
The resulting series are compared to the Arctic Oscillation Index, and a strong correlation with the major features is found. AO index is a zero mean series and was offset by 0.5 here to compare it to deviations of the freezing / melting periods from even six month interval between equinox dates.
The 20 day gaussian filter is similar to a 40 day triple running mean.